The charging method of smart devices is about to change dramatically. By 2024, the shipment of smartphone wireless charger systems is expected to exceed 1 billion units per year.
The consumer market is the global growth engine of wireless charger technology
According to a report by Maimus Consulting, in recent years, from smartphones to integrated applications in Starbucks coffee shops, wireless charger technology has attracted widespread attention from the industry. However, the development of the wireless charger market will still be highly unbalanced and will be mainly geared towards the consumer sector: for example, the number of consumer wireless charger receivers in smartphones is expected to exceed 1.2 billion by 2024, but pure electric and hybrid It is expected that wireless chargers for powered electric vehicles (EV/HEV) will not be applied in the market until 2022, and will not be selected by high-end cars until after 2022.
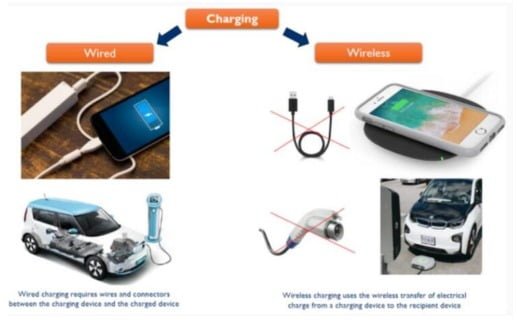
Wireless charger vs. wired charger
The general consumer market has the closest demand for wireless chargers, which is related to the popularization of consumer electronic products such as smartphones, smart earphones, and smartwatches. These smart devices require frequent chargers, so users are always surrounded by various charger cables. Since wireless chargers are still an “early” market demand, consumer wireless chargers may be a slow technology-driven market. However, due to the particularity of the market, technology integrators are very eager for new differentiating factors, and wireless chargers can play this role well. Therefore, the application of wireless chargers in this field is faster than expected.
In the smartphone industry, as well as in the consumer service and automotive markets, a slightly interesting feature can become a significant differentiation advantage and bring a huge revenue impact.
For example, a new set of Emoji expressions is enough to arouse users’ desire to buy new mobile phones, and whether coffee shops provide wireless charger services can also produce exactly the same effect.
Technology developers and integrators work together to promote the application of wireless charger technology, not only creating new markets but also rapidly cultivating markets. Wireless charger transmitters can now be seen in smart furniture, airport terminals, and restaurants, and cushions that can charge multiple devices in the comfort of home are also under development. In view of these innovations, the general electronics industry has been promoted towards wireless charger compatible solutions. In the future, as mobile phone manufacturers such as Apple bring more “wireless” smart devices to the mass market, today’s assumptions may become the standard in the future.
For other mass markets, the emergence of wireless chargers is definitely a “technology-driven” product.
This is especially true for electric vehicles. In this field, wireless chargers will only appear in high-end electric vehicles in the medium term, which is not yet very attractive to ordinary consumers.
In this report, Yole focuses on the differentiation of consumer and mobile markets, as well as the industrial, medical, and military markets where independent differentiation is important. This report provides market forecasts for each market segment and estimates the necessary wireless charger components.
Wireless charger, the driving force of the entire supply chain, air purifier power adapter
Two technologies shaping the wireless charger industry
For consumer electronics and future mobile applications, only two technologies are expected to be commercially applied in the next five years: induction chargers and electromagnetic resonance chargers. The two methods are similar in technology, but their characteristics are quite different.
Induction chargers require a strong coupling between the transmitter coil and the receiver coil, so the transmitter and receiver need to be very close to each other and in a specific location. This charger technology abandons the cable, but in the charger process, the use of the mobile phone does not bring any flexibility, and the mobile phone needs to be limited to a certain position. However, due to its maturity and relatively high efficiency, this is currently the only viable commercial option. Mobile phone manufacturers such as Apple are working hard to improve the charger efficiency of this technology and then transition to the next stage of wireless charger technology-electromagnetic resonance wireless charger.
Through the electromagnetic resonance charger, the transmitting coil and the receiving coil can be weakly coupled, but the operating frequency is similar. This allows the device to be used at a slightly larger distance from the charger area, thus increasing the degree of freedom of the charger location. This new charger technology is expected to be applied in consumer electronic products soon, and its existing prototype products can be used with mobile phones that support the Qi standard. Unfortunately, the electromagnetic resonance charger is still immature and low in efficiency. These two obstacles limit its market application.
Despite these shortcomings, the potential of electromagnetic resonance chargers still provides an attractive prospective market for GaN (gallium nitride) component manufacturers, allowing them to profit from electromagnetic resonance technology in the MHz range (such as the 6.78MHz band). It depends on whether the industry will switch from the current 105KHz~205kHz frequency band to a higher signal frequency.
Other technologies such as capacitive wireless chargers, laser chargers, and microwave chargers are still at the laboratory or prototype level and are limited to very specific applications such as military or aerospace.
We are unlikely to see these technologies successfully enter the consumer product arena soon.
This report deeply analyzes the physical and technical concepts of induction charger and electromagnetic resonance charger technology and discusses the physical characteristics and technology behind their decisive elements.
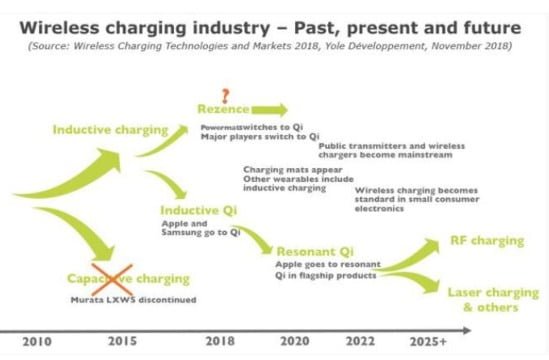
The past, present and future of the wireless charger industry of USB mobile phone charger manufacturers
The ecosystem is ready for mass production
Technical developers have effectively solved the complex technical problems of smartphones placed in strong electromagnetic fields, and in just a few years, a complete industrial chain focusing on mobile phone induction chargers has been completed.
It is worth noting that the value chain of inductive chargers is very similar to the developing electromagnetic resonance chargers. In fact, even if the physical mechanism is different, the two are very similar in technical content: both are composed of an inverter, a rectifier, a driver, a buck converter, and a coil.
In fact, most of the industry manufacturers are developing products of these two technologies at the same time. For example, Infineon Technologies (Infineon) provides samples of 6.78MHz electromagnetic resonance charger components and also provides semiconductor components for 105~205kHz induction chargers.
Although the application of wireless chargers is still in its infancy, the industry chain is already solid, and large semiconductor companies provide best-in-class electronic components. The diversity of manufacturers is now mainly reflected in the integration side, and wireless chargers are emerging in a variety of new systems from cars to smart furniture.
Technology integrators have already prepared for wireless charger applications. Brands that are usually not related to consumer electronics have appeared in this market: for example, Ikea (IKEA)
The HEKTAR desk lamp is equipped with a wireless charger transmitter, and Duracell (Duracell) is producing the Powermat wireless charger board for Starbucks.
These companies cooperate with electronics companies such as NXP (NXP), IDT, and Infineon to bring their solutions to the market mainly through a standard called Qi. In fact, the wireless charger standard originally started in two consortia: Wireless Power Consortium (the wireless power consortium, the development of the Qi standard) and the Air Fuel Consortium (the development of the Rezence standard). Now the Qi standard has established a dominant position and is used by most smartphones. Favored by manufacturers. Among them is Apple, which has tried to develop its own wireless charger standard.
In this report, Yole analysts analyzed the entire wireless charger ecosystem and provided the positioning of industry-related manufacturers in the field of wireless power transmission and wireless chargers in the future.
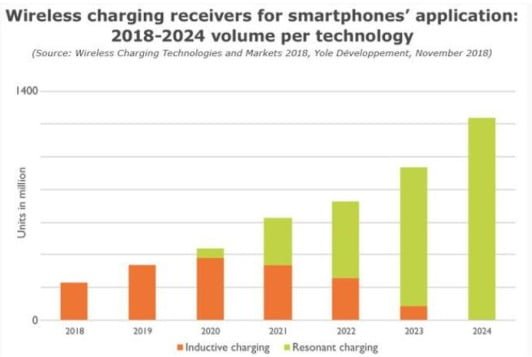
The market size of smartphone application wireless charger receivers segmented by technology from 2018 to 2024



